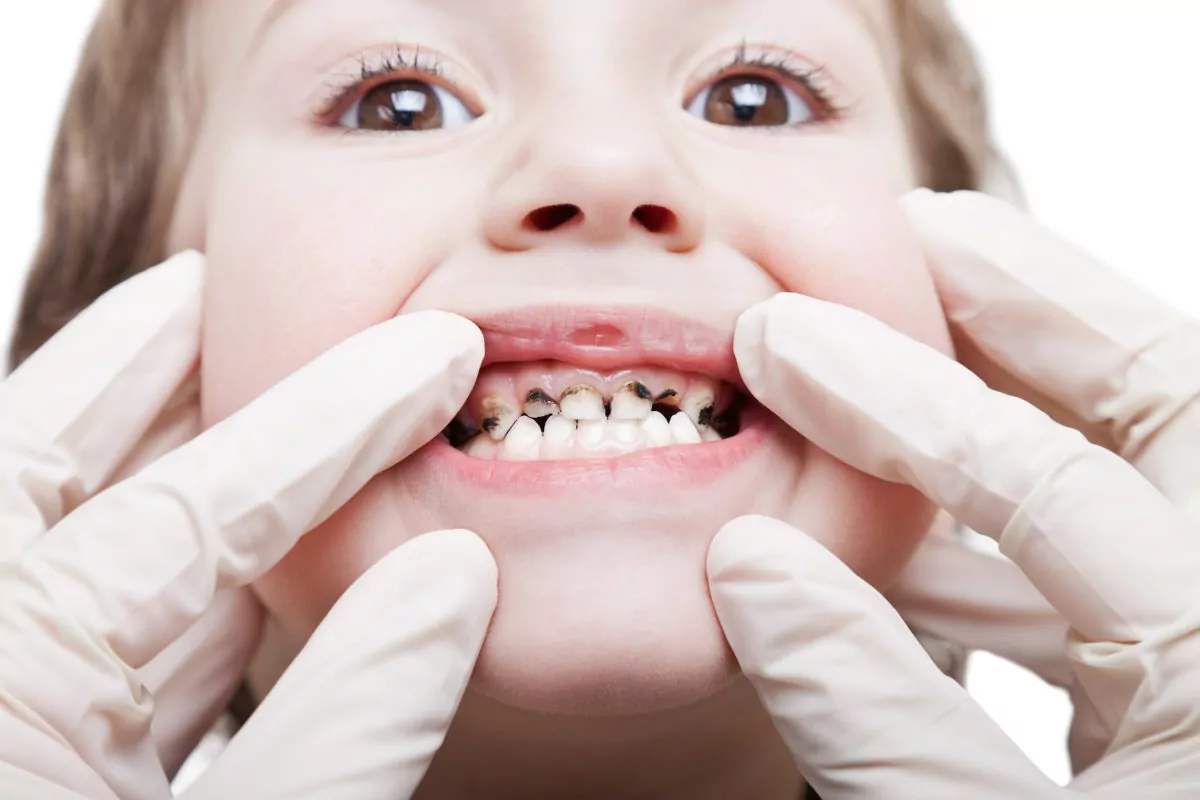
Tooth decay, especially in children, can turn into long-term oral health issues. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) regards tooth decay in children as a widespread (though often ignored) epidemic. Consider the CDC’s sobering statistics regarding oral health problems and tooth decay in children:
- About 1 in 7 U.S. adolescents have at least one decayed tooth.
- Approximately 1 in 5 U.S. children (aged 5-11) show signs of tooth decay.
- For families without a non-fluoridated water supply, tooth decay in children is twice as likely as families with fluoridated water.
- 52 percent of children (aged 6-8) have had tooth decay in their baby teeth.
There is plenty of bad news regarding tooth decay in children. The good news? If you know how to detect signs of tooth decay, your entire family will enjoy better oral (and superior) overall health!
The Super Dentists offers superior pediatric, orthodontics and parent dentistry services for your entire family. Regular visits will help prevent tooth decay in children.
What Is Tooth Decay in Children?
Tooth decay is the breaking down and destruction of tooth enamel, which is the hard outer surface of the tooth. If a child has tooth decay, it can lead to the early signs of cavities and cause holes to form in their teeth.
What Causes Tooth Decay in Children?
Tooth decay is caused mostly by bacteria, but other things can contribute to its development. A child may develop tooth decay if their teeth are not properly cleaned after eating foods, carbohydrates, or foods that mostly contain starches or sugars.
Some examples of foods that contain an abundance of sugars or starches include soda, milk, raisins, fruit juices, cake, bread, and cereals. Bacteria that typically live in the mouth change these foods on the teeth, making them acidic. The combination of food, acid, bacteria, and saliva in the mouth creates plaque, which sticks to the teeth.
Over a period of time, the acid that formed within the child’s mouth eats away at their tooth enamel, causing cavities to form.
There are also other risk factors for tooth decay in children. These include, but not limited to conditions that cause dry mouth (mouth breathing, medical issues or meds, etc), imbalance of the oral microbiome, and lack of certain nutrients such as vitamin D and vitamin K2 that are required for absorption of calcium.
Signs & Symptoms of Early Stage Tooth Decay
What are the early signs of tooth decay? Tooth decay can begin in children as young as six months to one year of age, so it is important to know how to help identify tooth decay early on. If you’re interested in knowing how to prevent tooth decay, you have to know what to look for. These signs and symptoms of tooth decay include:
- Gums and teeth sensitive to hot or cold foods. Sensitivity can be an early sign of decaying teeth When cavities start to form, they’re undetectable to the naked eye – but not for the teeth and gum nerve endings. Cavities start as small pits in the teeth, and as the enamel wears down, the interior nerves are subject to and react to certain foods and beverages.
- Bleeding gums. Gum disease often accompanies tooth decay and is a sign of rotting teeth. Bleeding gums are common with tooth decay in children. See your pediatric dentist if your child’s gums bleed for any reason.
- Discolored teeth. Small brown or black spots are often the sign of cavities and an early sign of tooth rot. You may also notice a dull white band on the surface of the tooth, close to the gum line, which is usually an early sign of rotting teeth.
- Foul breath. Foul breath is one of the early signs of teeth rotting. When too much bacteria builds up in the mouth, bad breath soon follows. And not long after that, tooth decay as well. Think of bad breath as an early warning sign of tooth decay.
- Toothache. A toothache is one of the most classic signs of early tooth decay in children. If a child complains of a toothache for several days, it can likely be due to tooth decay. Toothaches can come on without a warning or they can occur after eating or drinking.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay
Want to prevent tooth decay in children? Follow these four simple guidelines:
- Brush at least twice per day. SuperMouth has the right toothbrush for every age with cool features such as augmented reality and music to make brushing enjoyable. .
- Mind the diet. Excessive sugar consumption is the main culprit for tooth decay in children. Incorporate more veggies into your child’s diet. Sure, that’s easier said than done, but with creative & healthy recipes and snack ideas, anything is possible.
- Rinse after meals. This simple suggestion eliminates bacteria and plaque buildup.
- Floss on a regular basis. Have your child floss at least once every day. This habit is critical for lifelong dental health.
- Get enough hydroxyapatite and/or fluoride in your oral care products. Using a toothpaste and mouthwash with hydroxyapatite and/or fluoride regularly helps to toughen the enamel, making it difficult for acid to penetrate. Many toothpastes contain fluoride, and it is common for tap water to be fluoridated. Just make sure your child is able to spit the toothpaste out.
- Go for regular dental check ups. Children should see their dentist every six months for a regular exam, as well as teeth cleanings. Regular dental check ups not only help prevent tooth decay, but they can also help prevent gum disease.
How Is Tooth Decay Treated In a Child?
Tooth decay can be treated in children, but treatment depends on your child’s tooth decay symptoms, general health, age, and severity of the tooth decay. Most of the time, treatment involves removing the decayed part of the child’s tooth and replacing it with a filling.
Fillings, also known as restorations, are materials that are placed into the child’s teeth to help repair any damage from tooth decay. There are different types of fillings that can be suitable for children:
- Direct Restorations. This type of filling requires one visit to the dentist to place a filling directly into the prepared dhole. Direct restorations can be made out of resin, silver, acrylic acids, or fine glass powders. Most of the time, they match the color of the child’s teeth.
- Indirect Restorations. This type of filling requires at least two visits to the dentist. These fillings include onlays, inlays, crowns, veneers, and bridges. Indirect restorations can be made of gold, ceramics, base metal alloys, or composites and often look like natural tooth enamel.
Visit The Super Dentists – We’ll Help Prevent Tooth Decay in Children
If you detect early signs of tooth decay, schedule an appointment today at any of The Super Dentists six locations in San Diego. You can also call (855) GO SUPER or text us at (844) 765-1234. Thanks for visiting The Super Dentists, San Diego’s premier pediatric dentists!